China has dominated the production of rare earth metals – the vital inputs in the clean energy transition as well as military equipment. But this could be all set to change as Western economies seek greater control and to reduce their dependence.
By Marion Laboure, Director at Deutsche Bank Research.
At an investor day in early March, electric vehicle manufacturer Tesla stated its intention not to use rare earth metals (‘rare earths’) in their next generation of electric vehicles, citing health and environment risks associated with their extraction. 1
Power of attraction
Other automobile producers have also indicated they are trying to stop or reduce their use of these rare earths. The most common way of powering electric vehicles is by rare-earth magnets, the NdFeB magnet made using the rare earth metal neodymium. According to the European Raw Materials Alliance (ERMA), about 5,000 tonnes of rare earth permanent magnets were used in EVs in 2019, and it is forecasted that this number may rise to between 40,000 and 70,000 tonnes on a global level by 2030. These magnets are preferred as they allow for a more lightweight, compact design, and greater efficiency as they do not require an external power system to generate a magnetic field, such as in asynchronous induction motors.
Rare earths are essential raw inputs used to manufacture more than 200 commercial products, such as defence equipment, semiconductors, green energy infrastructure (such as wind turbines), as well as everyday consumer goods such as mobile phones, cameras, computer drives, floodlights and microwave filters. They significantly improve the performance, efficiency, longevity and reliability of technology due to their unique chemical, electromagnetic, electro-optical, nuclear and magnetic properties.
And, as the global economy begins to undertake its clean energy transition, rare earths will become increasingly important. In 2020, the World Bank found the production of critical minerals, including rare earths, could increase by nearly 500% by 2050 if demand for clean energy technology continues to accelerate.
However, the global supply chain for these rare earth metals is fragile and vulnerable to geopolitics. This article takes a closer look at competition and supply risks.
Chokepoints in the rare earths industry
Despite the name, rare earths are not that rare. They can be found in subsoils throughout the world, including in the US. However, economically exploitable deposits in the earth’s crust are in fact rare. According to the United States Geological Survey, the greatest percentage of mineable deposits are found in China (35%), Vietnam (18%), and Russia (17%).
As a consequence, the most accessible rare earth metals are in geopolitical choke points and situated within the boundaries of non-US allies. China dominates the production of rare earths, producing 70% of the world’s rare earths in 2022. Meanwhile, the US imported 74% of its rare earth compounds from China in 2022 and with US-China tensions continuing, competition for rare earth metals is heating up, and supply risks are accelerating. In the most recent development in September 2023, Malaysia has announced its intention to develop a policy to ban exports of raw rare earth materials in order to maintain a foothold in the more high value add segments of the supply chain, such as rare earth processing.
The EU imports 98% of its rare earths components from China, and because of this, the discovery of 11 million tonnes of rare earth oxides by Sweden’s state-owned mining company LKAB on 12 January 2023 represented an important development for the EU’s domestic industry. In a press conference, LKAB chief executive Jan Moström said, “This is the largest known deposit of rare earth elements in our part of the world, and it could become a significant building block for producing the critical raw materials that are absolutely crucial to enable the green transition. We face a supply problem. Without mines, there can be no electric vehicles.” He added that it would take “several years to investigate the deposit and conditions for profitably and sustainably mining it” and 10-15 years before raw materials are delivered to the market.
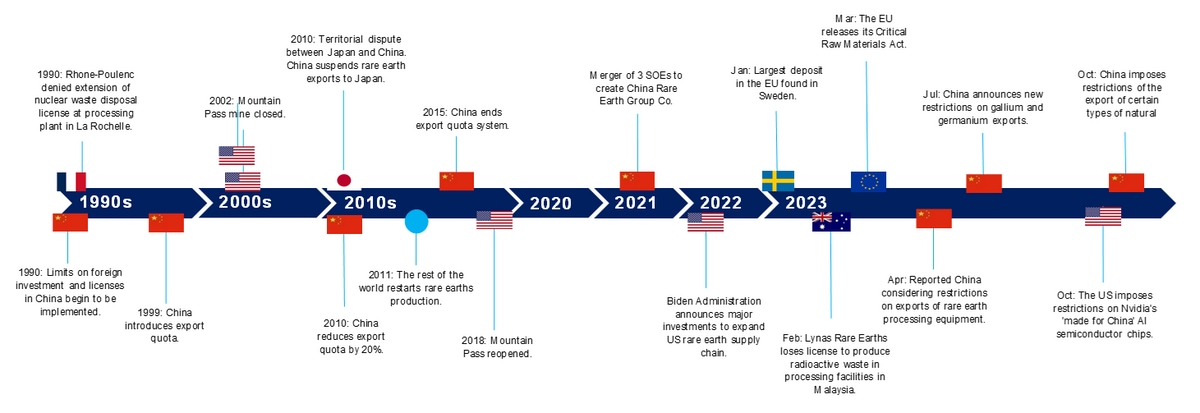
Figure 1: Timeline of the global rare earths industry
Source: Deutsche Bank.
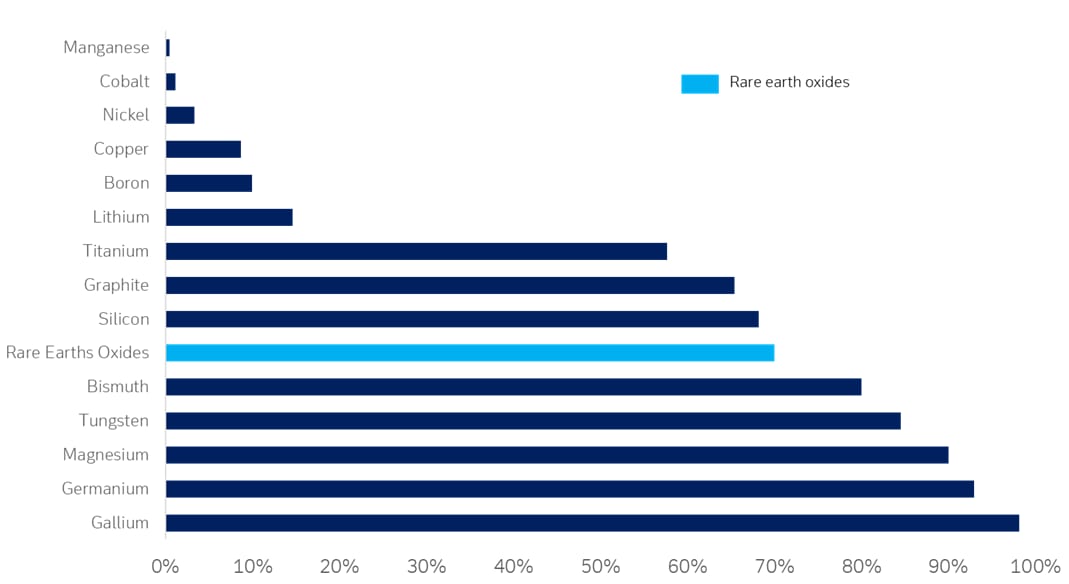
Production of rare earths requires complex know-how and highly sophisticated processing facilities – competencies China has been steadily acquiring for decades. China is already the largest producer of most critical minerals – including rare earths (see Figure 2)
Figure 2: China’s relative share of global strategic raw material production (2022)
Sources: Deutsche Bank, World Mining Data, United States Geological Survey. Note: The above minerals are those identified as strategic by the EU's 2023 Critical Raw Materials Act update. Where data was not available with the 2023 United States Geological Survey, 2021 data from World Mining Data was used.
In most deposits, the different rare earths are combined with each other as well as other minerals. Due to the chemical similarity of the different rare earth elements, the separation process is very complicated – and can differ by deposit and location because of this.
Processing involves many stages of physical and chemical treatments, consuming significant amounts of acid and water, driving up costs. The radioactive by-products of rare earths processing remains a key concern – France closed a processing plant in 1990 and the Malaysian government in early 2023 requested that the Australian mining company Lynas Group Metals remove cracking and leaching from its operations as a condition of its license renewal. Lynas has since be awarded an extension of its operating license, which allows it to import rare earths containing radioactive material, until March 2026.
This is why LKAB’s Jan Moström estimated it would take some years to establish how to sustainably mine the rare earths from the newly discovered deposits.
Energy transition
According to the International Energy Agency, “the global clean energy transitions will have far-reaching consequences for mineral demand over the next 20 years” and it notes that “wind power plays a leading role in driving demand growth due to a combination of large-scale capacity additions and higher mineral intensity (especially with growing contributions from mineral-intensive offshore wind)”.3
To achieve climate neutrality by 2050, the EU will most likely require between 7 and 26 times more rare earths; an increase of between 700% and 2,600% of neodymium, dysprosium and praseodymium.4 And while alternatives to the NdFeB rare earth permanent magnet are being sought by electric vehicle producers, no perfect substitute has yet been discovered or invented. The EU will also require 35 times more lithium. If US-China rare earth tensions continue, or if the EU does not secure a greater supply of rare earths, this could compromise the EU’s green ambitions.
In short, rare-earth magnets are essential for the energy transition and by 2030, magnets are expected to drive 40% of total demand for rare earths.
It is no surprise therefore that Western economies are ramping up initiatives to invest in rare earth production, as well as recycling and reshoring of permanent magnet production. In the long run, we could well see an end to China’s dominance of supply and there could even be a reshuffling of the current geopolitical hegemony.
1 See reuters.com
2 See asia.nikkei.com
3 See iea.org
4 See eurometaux.eu
The views expressed on these pages are those of the authors and/or the institution they represent, and not necessarily those of Swift.